What do you know about human parasitic diseases? The variety of human parasites is not limited to internal helminths.
There are certain types of parasites that penetrate and live under the skin of a person, causing the same unpleasant symptoms as internal parasites.
In addition, the variety is not limited to helminthiases alone - there are ticks, insects, and protozoa.
Each of them has certain symptoms and manifestations that you should be aware of.
It is also equally important to know how to get rid of subcutaneous parasites.
Varieties of parasitic skin diseases
What kind of parasites can live under human skin? The most diverse, including insects, helminths, ticks and protozoa unicellular organisms. Lesions of the human skin by various types of parasites are distinguished into a separate category of parasitic diseases.
Each group of diseases is united by characteristic pathogens:
- The simplest organisms cause protozoal skin diseases.
- Ticks cause acariasis of the skin.
- Insects can cause entomotic skin lesions.
- Helminthiases develop as a result of infection with helminths.
All these pathogens of human skin parasitic diseases are equally unpleasant and require diagnosis and treatment. Long-term neglected forms can lead to irreparable consequences from blindness to death. Fortunately, it can be added that most of the list of parasites living under the human skin is characteristic mainly of countries with hot and humid climates.
Diseases caused by protozoa
Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is caused by the simplest, single-celled pathogens carried by mosquitoes. A person infected with leishmaniasis becomes a reservoir for the further spread of the infection. After being bitten by a mosquito, which is the main host of Leishmania, a person develops cutaneous or visceral leishmaniasis. Cutaneous leishmaniasis manifests as deep ulcers or pustules and extensive skin lesions. The mucocutaneous form of the disease leads to significant deformations of the appearance, especially of the face. Airway edema in leishmaniasis can be fatal.
Leishmaniasis occurs in 90 countries of the world and is a very common disease in Syria, Iran, Afghanistan, Saudi Arabia, Brazil, Peru.
Diseases caused by ticks
Demodecosis
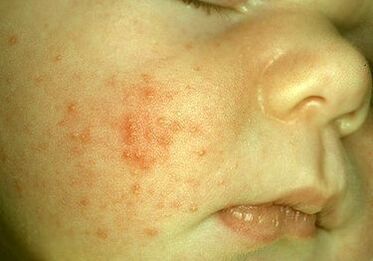
A disease caused by a parasite that lives under the skin in the sebaceous glands and follicles of human living hair. This is a microscopic mite - demodex. It is mainly localized on the eyelids, facial skin, and auditory canals. Rarely - on the chest and back.
Demodex damage causes complicated acne, dermatitis, which is exacerbated in spring and autumn. The skin looks red, hyperemic, bumpy, inflamed. The ciliated edge of the eyelid is usually swollen, red, the eyelashes are stuck together, along the edge of the eyelid there are discharge in the form of crusts, and eyelash loss is characteristic. Sometimes the disease proceeds without obvious manifestations, therefore the tick is considered conditionally pathogenic. Usually, demodicosis is exacerbated in people with impaired immunity, with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and metabolic disorders.
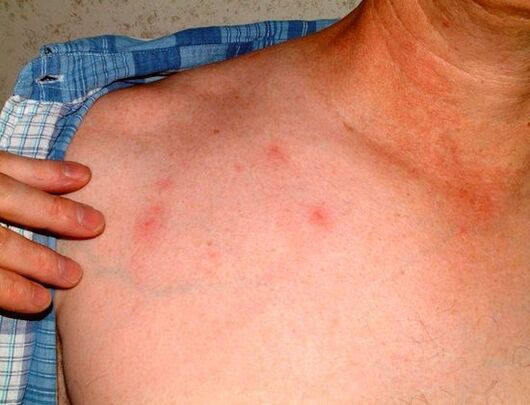
Scabies
Another ubiquitous disease caused by mites called itch itching. These mites gnaw passages in human skin, in which they lay eggs. The development of an adult tick is accompanied by a complex cycle. Usually this process occurs at night, so the itching of the skin intensifies at this time. The main diagnostic symptom of the presence of parasites under the human skin looks like double red small dots located nearby. These are double passages gnawed by a tick.

The disease is complicated by various infections that the patient brings in trying to relieve the itching: streptoderma, nodular seals, blood crusts around scratches, rashes in the form of bloody blisters and other skin lesions. Complicated scabies can resemble urticaria, pyoderma, dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis.
Infection usually occurs through prolonged contact with sick people (it has been proven that scabies requires skin-to-skin contact, lasting up to 30 minutes; you should not discard the rather low probability of infection when using common household items).
Diseases caused by insects
All skin diseases caused by dipterans are collectively called myiasis.
Wolfartiosis
The disease is caused by an insect called wolfarth fly, which lays the larvae in mucous membranes or wounds on the human body. The larvae destroy tissues, releasing a special enzyme, causing severe pain, necrosis, edema, pus and gangrene of the affected tissues. They usually parasitize in the eyes, nose and ears. The wolfarth fly is widespread in countries with hot and temperate climates.
Diseases caused by helminths
Dirofilariasis
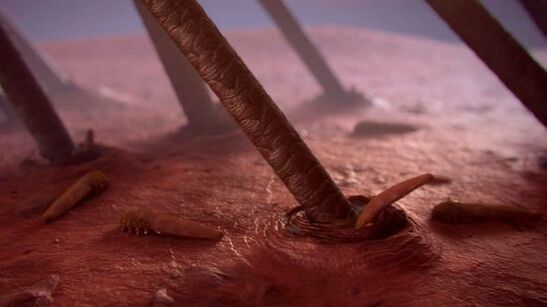
A disease caused by round helminths. The source of infection is domestic animals - cats and dogs. The carrier is a mosquito. After its bite, sexually mature individuals of nematodes begin to develop in the human body, which, as a rule, parasitize under the human skin. The insect bite becomes denser, inflamed and itchy. A characteristic feature of the pathogen is its ability to move under the skin, therefore, the disease is accompanied by a feeling of movement, crawling inside the inflamed seal. Sometimes a nematode can be seen under the skin, cases of an individual emerging from the mucous membrane of the eye are described.
Allergic reactions, fever, nausea, and weakness can be accompanying symptoms.
Strongyloidosis
A disease caused by parasite larvae that invade a person's skin should he walk with bare feet on the ground. Strongyloidosis foci are found in Georgia, Ukraine, Krasnodar, Stavropol Territory. The roundworm larvae invade through the skin and migrate underneath, causing redness, itching of the skin and the development of red blisters.
Treatment recommendations
General recommendations have been developed for the treatment of diseases caused by one or another human subcutaneous parasite. The most relevant for our region is the treatment of strongyloidosis, scabies and demodicosis. Treatment is prescribed after the diagnosis of the disease and only by a specialist. Some complications and manifestations of the disease require an individual approach to treatment.
- Helminthiasis is recommended to be treated with antiparasitic drugs.
- For the treatment of itch itching, ointment, cream and other effective remedies are used. In the fight against scabies, a treatment regimen and a system of preventive measures for contact persons have been developed.
- Demodex treatment is carried out with complex measures to strengthen the immune system, treat gastrointestinal diseases and other procedures. Ointments for the treatment of scabies are used directly for the skin, as well as various cosmetic procedures.
Subcutaneous parasitic diseases require efforts to be treated, so it is best to prevent infection by applying basic rules of personal hygiene. It is not superfluous to know the common symptoms that accompany such diseases, so as not to come into close contact with sick people.